Deviation and Dispersion of Light by a Prism
Deviation and Dispersion of Light by a Prism: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Angle of Prism, Deviation from Small Angle Prism, Chromatic Aberration & Thick Lens etc.
Important Questions on Deviation and Dispersion of Light by a Prism
What is thick lens? How it is different from the thin lens?
The focal length of a thin convex lens is _____ than that of a thick convex lens.
A concave lens is always tapering at edges and thicker in the middle.
What are thick lens?
The rays of different colors fail to converge at a point after going through a converging lens. This defect is called _____.
Which of the following has a larger chromatic aberration?
What causes Chromatic aberration in lenses?
A ray of light passes through an equilateral prism such that angle of incidence is equal to angle of emergence and the latter is equal to of the angle of prism. The angle of deviation is (in)
Find angular dispersion due to glass prism of refracting angle . Refractive index for red and violet light is given as and respectively.
If the yellow light is refracted by a prism at an angle of minimum deviation then-
If the retractive index vs wave length for a thin prism be as shown in figure. Then the graph of angle of deviation vs graph is best represented by
Calculate the dispersive power for crown glass from the given data
and
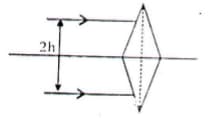
Two identical thin isosceles prisms of refracting angle 'A' and refractive index m are placed with their bases touching each other. Two parallel rays of light are incident on this system as shown. The distance of the point where the rays converge from the prism is
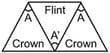
The respective angles of the flint and crown glass prisms are and . They are to be used for dispersion without deviation, then the ratio of their angles will be
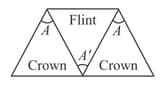
Three thin prisms are combined as shown in diagram. The refractive indices of the crown glass for red and violet rays are and respectively and those for the flint glass are and respectively. The ratio for which there is no net angular dispersion
Three thin prisms are combined as shown in diagram. The refractive indices of the crown glass for red and violet rays are and respectively and those for the flint glass are and respectively. The ratio for which there is no net angular dispersion
A ray of light is incident at an angle of incidence i, on one face of a prism of angle A (assumed to be small) and emerges normally from the opposite face. If the refractive index of the prism is μ, the angle of incidence i, is nearly equal to
